In the United States, the number of obese older adults has reached disturbing heights—now affecting approximately 20 percent of those ages 65 and older—and is only expected to rise as more “baby boomers” become senior citizens.
Weight loss through calorie reduction or exercise is generally good for most people as an intervention in obesity, although the appropriateness of these methods has historically been a matter of controversy in older adults who are overweight.
A major concern with weight loss for seniors is the accompanying loss of lean tissue, which can accelerate existing sarcopenia (age-related loss of muscle and strength). The result could also include reduction of bone mineral density that could worsen frailty and lead to greater risk of bone fractures and broken hips. Studies have yet to provide sufficient evidence, one way or another, as to whether or not weight loss provides a true enhancement to quality of life.
In a one-year, randomized, controlled trial, researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis evaluated independent and combined effects of weight loss through calorie reduction and exercise in nearly 100 obese older adults with an average age of 70. The study, published in the March issue of New England Journal of Medicine, randomized subjects into one of four groups:
- Control group – participants of which did not receive any advice to change diet or activity.
- Diet group – followed a reduced-calorie diet (deficit of 500 to 750 calories per day) with high-quality protein (1 gram per kilogram of body weight per day).
- Exercise group – maintained weight and exercised three times weekly, which included 90 minutes of aerobic exercises, resistance training, and flexibility and balance exercises.
- Diet-exercise group – combined weight management instructions and exercise trainings as described in 1 and 2.
To “even the playing field” and reduce confounding variables, the researchers gave participants 1,500 milligrams of calcium and 1,000 IU of vitamin D as supplements per day.
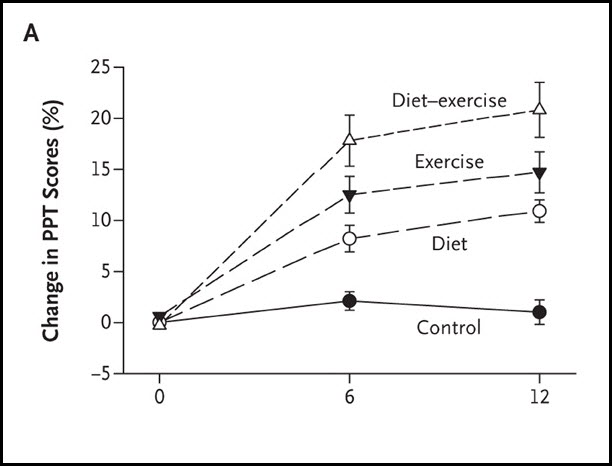 Results from this carefully designed study show the “diet-exercise group” preserved more lean muscle and bone density when compared to the other groups. They also gained significantly better physical function and were less frail than other groups, outperforming in all measured parameters. (See Figure A: Results of Physical Performance Test (PPT).)
Results from this carefully designed study show the “diet-exercise group” preserved more lean muscle and bone density when compared to the other groups. They also gained significantly better physical function and were less frail than other groups, outperforming in all measured parameters. (See Figure A: Results of Physical Performance Test (PPT).)
“Weight loss combined with regular exercise may be beneficial in helping obese older adults maintain their functional independence,” the authors wrote.
Engaging in a variety of exercises, such as aerobic exercises, resistance training, and flexibility exercises is essential for healthy aging. Most older, obese adults are able to safely engage in regular physical activity; however, because fitness levels vary, a medical professional is important to determine which exercises are appropriate for an individual’s specific needs. Certain medical conditions, as well as medications, can also affect a person’s tolerance for exercise.
Aerobic Exercise
Moderate intensity aerobic exercise, 30 minutes a day, five times per week is currently recommended for adults ages 65 and older, according to the guidelines presented by the American College Sports of Medicine (ACSM). Those who are not used to exercising can start out with a shorter duration at a lower intensity and work up to the recommendations.
Aerobic exercise can lead to improved cardiovascular function, better quality of sleep, improved mental health, weight loss, and enhanced immune function. Suggested aerobic activities for older adults include low-impact exercises such as walking, biking, low-impact aerobics, and water activities such as swimming or water aerobics.
Resistance Training
Resistance training is essential to preserve lean muscle and bone density or even regain lost muscle. Seniors should perform resistance-training exercises two to three times weekly. The trainings should consist of 8 to 10 different strength exercises with 8 to 12 repetitions each. Again, it’s best to start out slow, with lighter weights and fewer repetitions.
There are many different types of strength training exercises and a variety of equipment that can be used, including weight-training machines, dumbbells, resistance bands, medicine balls, or weighted bars.
It’s best to work muscles to the point of fatigue, without overstraining, while taking enough time between workouts to allow the muscles to rest and recover. (Some examples of strength training exercises can be seen in Kathy Coover’s at-home workout. See KC Workout.pdf.)
Flexibility Exercises
Flexibility and balance are also factors important to health that decrease with age. Leading a sedentary lifestyle can cause connective tissues to weaken and joints to stiffen. Ultimately, the lack of activity affects a person’s range of motion, balance and posture.
Performing stretching exercises regularly can help improve flexibility and increase freedom of movement. Every workout should begin and end with proper stretching exercises to help warm up and soothe the muscles. Stretching, along with strength exercises, can also improve balance, which can help reduce the risk of falling, particularly important for elderly individuals.
Seniors (or anyone, really) should be sure to warm up to get blood flowing before stretching and then hold each stretch for 20 seconds to help avoid injury.
Final Word
It’s never too late to begin a weight-control and exercise program. Along with a healthy diet, engaging in individually-appropriate physical activity—aerobics, resistance training, and flexibility exercises—can provide seniors a way toward feeling younger.
Reference: Villareal DT, Chode S, Parimi N et al. Weight loss, exercise, or both and physical function in obese older adults. N Engl J Med 2011;364:1218-29.
Related posts:
- How to Get to Your Healthiest BMI with Isagenix
- Omega-3 Slows Muscle Loss in Older Adults
- Study – High Vitamin D Linked to Muscle Strength in Elderly
- IsaLean Shake: The Power for Staying Lean, Battling Aging
- Three Critical Nutrients for Stronger Bones
- Are You Losing Muscle As You Age?
- How to Lose Weight Safely If at High Risk of Gallstones





